Science fiction takes us to new social, cultural and technological lands, but often it also transports us to new worlds in the more literal sense, that of faraway planets rich in excitement and imagination.
Before the 1990s, the idea of planets around other stars was science fiction, but today, astronomers are discovering thousands of ‘exoplanets’, and inevitable comparisons with the worlds of science fiction have been drawn. For instance, the phrase ‘Tatooine planet’, to describe a world with two suns, is practically part of the scientific lexicon now.
So here are four fictional, yet scientifically plausible, planets – and four real planets that show that, sometimes, truth is stranger than fiction.
Blueheart

Water-worlds may be among the most common types of planet out there, so it’s no surprise that they’ve featured in science fiction. One of the most well thought-out is Blueheart, from Alison Sinclair’s 1996 novel of the same name. Ninety-seven percent of Blueheart’s surface is covered by a deep ocean, and is inhabited by genetically-engineered humans called adaptives. However, there’s conflict with a group of un-modified humans who want to terraform Blueheart to better suit themselves.
What’s really intriguing about Blueheart’s ocean is its false bottom, formed from floating forests that have dense, entangled roots that can catch nutrient-rich organic material sinking from the surface waters, maintaining the stock of nutrients necessary for ocean life. On Earth, the wind blowing off continents moves surface water away, allowing deeper water to well up to the surface, and this mixing keeps nutrients in circulation. Blueheart doesn’t have any continents, so the floating forests are the only way to prevent the nutrients from sinking to the sea floor, but here’s the rub: the floating forests can only form thanks to tides and breakers produced by the terraformers who threaten the adaptives’ way of life, hence the conflict at the heart of the story.
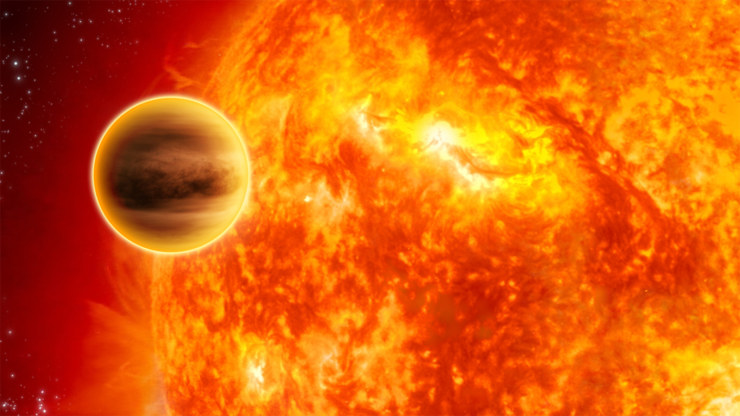
Real-life planet: Although Earth is the only planet we know that definitely has oceans of water, several strong candidates for ‘water worlds’ have been discovered, not least a planet 48 light years away called Gliese 1214b. The density of this planet suggests that three-quarters of it is composed of water, wrapped around a small rocky core. The water wouldn’t remain liquid all the way down to the core. Instead, the increasing pressure with depth would gradually transform the water into various exotic states. These might include ‘superfluid’ water with zero viscosity (friction between fluids) allowing whirlpool vortices to spiral forever, as well as exotic ‘ice VII’ that forms under incredible, crushing pressures of over 21,000 atmospheres.
Gethen

From Ursula K. Le Guin’s famous, award-winning novel The Left Hand of Darkness comes this planet of Winter (‘Gethen’ means winter in its inhabitants’ language). Gethen is in the grip of an ice age, with polar caps extending as far as 45 degrees north and south, and the entirety of the planet is cold. Scientists refer to this as a Snowball Earth state, triggered in part by Gethen’s highly eccentric orbit around its star (meaning that its orbit is not circular, but elongated), which can lead to long periods of runaway cooling.
Real-life planet: All planets, including Earth, have eccentric orbits, but most are only slightly eccentric. Gethen’s orbital eccentricity is a more extreme, but it’s got nothing on the gas giant planet HD 80606b, which is 190 light years away from Earth, and which has a 111-day orbit so extremely elliptical that it makes a closest approach of its star at a distance of just 4.5 million kilometers, whipping past it in a matter of hours. (For comparison, Earth is 149 million kilometers from our Sun). During this fast summer, its temperature rises from about 500 degrees C to 1,200 degrees C, triggering huge summer storms with winds blowing at 15 times the speed of sound. Then the planet moves quickly away from its star and back out into deep space to begin another orbit.
Trisolaris

This deadly world from Liu Cixin’s The Three Body Problem is gravitationally thrown around a system of three stars like a hot potato, leading to catastrophic Chaotic Eras where the planet bakes or freezes, interspersed by short-lived Stable Eras where civilization can arise once more. It’s purported to be the Alpha Centauri system, which is the closest star system to Earth, just 4.3 light years away. However, the Trisolaran system doesn’t quite match reality: Alpha Centauri is a double-star system with Proxima Centauri a possible third member (astronomers aren’t sure if Proxima is gravitationally connected, or just passing by) and the orbital dynamics are much more stable. Astronomers have even found a planet orbiting Proxima, but this rocky world has probably been irradiated by its star.
Real-life planet: While the interchanging gravitational fields of Trisolaris’ three stars causes its chaotic motions, in real life no known ‘Tatooine planets’ are as unstable. However, a star’s gravity can affect a planet in other ways.
WASP-12b, which is 800 light years away, is a gas giant planet orbiting just 3.4 million kilometers from its star. This is close enough for gravitational tides from the star to stretch WASP-12b into an egg-shape, far broader around the equator than around the poles. The planet swelters at 2,200 degrees C and is evaporating under the intense stellar heat and radiation, losing 189 quadrillion tonnes of gas from its atmosphere every year, the gas bleeding away like the tail of a comet.
Arrakis

Better known as ‘Dune’ from Frank Herbert’s novel, Arrakis is a desert world and the only source of the spice melange, which the Spacing Guild uses to fold space and travel interstellar distances. The only water on Arrakis is found in tiny ice caps at the poles and in underground reservoirs.
Planetary scientists have actually theorized the existence of such worlds, describing Arrakis as “a bigger, warmer Mars … [with] signs that water flowed in the prehistoric past”. The scientists suggest that these Dune-like worlds could remain marginally habitable over a wider range of distances from their star than wet Earth-like planets can.
Real-life planet: On Arrakis, spice is more common than water. On the planet 55 Cancri e, which is the fifth planet in orbit around the star 55 Cancri, located 41 light years away, carbon is more common than water (and, hence, oxygen), a characteristic that could lead to a seriously weird world. Its landscape could be made of chiseled graphite, while the high-pressure carbon in its core could be transformed into an enormous chunk of diamond the size of a small planet.
For more information on how astronomers discover new planets, visit NASA.
Keith Cooper is a science journalist, Editor of Astronomy Now magazine, and author of The Contact Paradox: Challenging Our Assumptions in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (Bloomsbury Sigma). Follow Keith on Twitter.










Neat!
I recently read Ray Jayawardhana’s Strange New Worlds, which wraps up with a (gently speculative) introduction to astrobiology, or ‘okay, if any known exoplanets host life, how would we know and what could it look like?’. It felt like SF in reverse.
Alan Dean Foster has fun with exotic-ish planets. Tran-ky-ky being an ice planet, and Cachalot the ocean planet.
When it comes to weird planets, not many people hold a candle to Larry Niven.
I am 99% sure that Cixin Liu’s Trisolaris is dynamically impossible. If the orbits are so chaotic on a human timescale one of the bodies would have been ejected from the system long before the planet had a chance to evolve life. The novel was interesting about Chinese society but the science was so bad I couldn’t finish it.
@@.-@ 0 have to agree with you about Trisolaris. It’s difficult to see how such an unstable environment would allow complex life to arise, let alone persist. That threw me right out of the novel, although I thought that his idea of unpeeling the electron was neat and original. But then, subatomic physics isn’t my field and a physicist might find this absurd and be thrown out of the story the way I was at the idea that anything above the level of a prokaryote would survive the loss of part of its planet’s mass.
Gethen has always bothered me. I find it difficult to imagine how it would be climatically stable, as it appears that even the equatorial regions are at best temperate in climate. During Earth’s last continental glaciations, the equatorial regions were still torrid, at least at low elevations – terrestrial humans didn’t have to acquire the sort of adaptations to cold seen in the Gethenians. If Gethen was glaciated to the extent described, and the equatorial regions were as cool as they appear to be, then it’s hard to see why the continental glaciers weren’t in the process of sliding right to the equator. LeGuin gives us a bit about solar output and how, with a little less of it, this might just happen, true.
One thing that I didn’t get out of Blueheart was just how you would go about terraforming a water world. Gin up plate tectonics, perhaps? Or did I miss something here.
For the real-real stuff you may want to check this anthology:
A Kepler’s Dozen: Thirteen Stories about Distant Worlds That Really Exist
“…stories all based on real planets discovered by the NASA Kepler mission…”
For those who read Russia: Boris E. Shtern (Борис Евгеньевич Штерн), the novel Ice Shell (Ледяная скорлупа; 2018) – technical/scientific triller following how intelligent aliens on Jupietr’s moon Europa emerge from the subsurface ocean into space. Great stuff about human spirit and inquisitiveness, even though the characters are not human, of course. Stern is an astrophysicist himself.
Last but not least, my fellow Bulgarian: the novel Photon starship (Фотонният звездолет) by Dimitar Peev (Димитър Пеев) about an expedition to Proxima. The crew eventually discover a planetary system of hundred or so relatively small bodies, it appears the triple nature of the star didn’t allow the form large bodies, not even around Proxima. Furthermore, the Proxima system have two types of planets – “native” that are orbiting in more or less the same plane (as the solar system) and “visitors” that can have any orbital inclinations – there seem to have been scattered bu Alpha Cen A and B. Very facinating novel, written all the way back in 1964. Peev had a degree in law but spent almost all his life as a science journalist.
I really hope one day the automated translation algorithms will become good enough to translate fiction at passable level, because I don’t see a way any of this stuff being translated into a foreign language. For reference, Peev’s (and mine) native language, Bulgarian, is spoken by about 8 mln people, if you count the diaspora in US, Germany, Russia, Spain, etc.
The undisputed master of bizarre-planet SF is Hal Clement, who wrote back in the 1950s. Amazing stories, like Mission of Gravity, set on a rapidly-spinning giant planet with a surface gravity of 2g at the equator and 600g at the poles, inhabited by centipede-like indigents; and Close to Critical, set on a planet with an atmosphere close to the triple point of water; and Iceworld, about a visit to an inhabited planet much too cold for the explorer; and so on for many other worlds. All fascinating reads!