It’s a question that has haunted every Narnia fan: WHY TURKISH DELIGHT? Why would Edmund Pevensie willingly sell his family (and, allegorically at least, his soul) to the White Witch for boxes of candy? I mean:
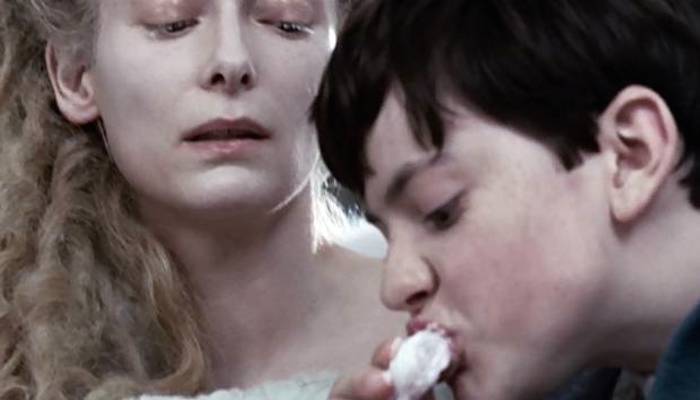
While he was eating the Queen kept asking him questions. At first Edmund tried to remember that it is rude to speak with one’s mouth full, but soon he forgot about this and thought only of trying to shovel down as much Turkish Delight as he could, and the more he ate the more he wanted to eat, and he never asked himself why the Queen should be so inquisitive. She got him to tell her that he had one brother and two sisters, and that one of his sisters had already been in Narnia and had met a Faun there, and that no one except himself and his brother and his sisters knew anything about Narnia. She seemed especially interested in the fact that there were four of them, and kept on coming back to it.“You are sure there are just four of you?” she asked. ‘Two Sons of Adam and two Daughters of Eve, neither more nor less?” and Edmund, with his mouth full of Turkish Delight,turkish-delight kept on saying, “Yes, I told you that before,” and forgetting to call her “Your Majesty” but she didn’t seem to mind now.
Seriously, Edmund, would you have handed Churchill over if she offered you a Mars bar?
The question of Turkish Delight often becomes still more perplexing when a young Narnia fan actually eats the stuff, and finds that it does not live up to Edmund’s rapturous praises. As with so many things in pop culture, the answer lies in the context, and since we’re living in a beautiful future, an academic article has stepped in to tell us all about the importance of Delight.
According to food critic Cara Strickland, the Turkish sweet cast an intoxicating spell over late-Victorian England. Made from a confection of rose oil and sugar, the candy is simple on paper, but proves extremely difficult to make – no matter how Western Europeans tried, they never quite replicated it. Thus, if you wanted real Delight, you had to import it from Turkey, which got expensive fast, so that it became a marker of either status or indulgence in much the way the way coffee had a century earlier.
Of course just as costs had gone down, the outbreak of World War II and its subsequent rationing meant that the candy was harder than ever to come by. Perhaps this is why it became so significant to Lewis? As he welcomed refugee children into his Oxford neighborhood, he thought back on the candies and holidays that had marked his own childhood.
It makes sense that Turkish delight would have been on Lewis’s brain as he crafted a book where Christmas features as a main theme. In Narnia, it is “always winter and never Christmas,” a product of the White Witch’s evil magic. It makes sense to draw a parallel between this dismal fantasy and the stark realities of wartime. Rationing extended to timber, which made Christmas trees harder to come by, and confectionery rationing didn’t end until February of 1953—still well before the end of sugar rationing later that year. When the White Witch asks Edmund what he’d like best to eat, it’s entirely possible that Lewis was answering for him: the candy that would be most difficult and expensive to obtain. Edmund isn’t just asking the witch for candy, he’s essentially asking her for Christmas, too.
As you see, asking WHY TURKISH DELIGHT? is not a frivolous question at all. Head over to Strickland’s full article to learn more about the making of Turkish Delight, and why it took British pop culture by storm.










Wondered the same thing, and have looked into it previously. Discovered that Turkish delight bought on either side of the Atlantic differs considerably, so you’ll have a different experience sampling this for yourself depending on where you live.
And even without all that interesting historical stuff, I’d choose Turkish Delight over chocolate literally every day of the week and twice on Sunday.
I’ve had what passes for Turkish Delight in both the UK and the US, but when I had the real thing from Turkey (brought back by a colleague from the very place), I finally understood what all the fuss was about. Whole different animal and worth giving up secrets for.
I had (or thought I had) Turkish Delight once and it was nasty stuff. After reading your article, I realize it might have been low-grade imitation. Maybe we should try the real Turkish imports before deciding that Lewis made a critical gustatory error.
I believe that the Turkish Delight given to Edmund was enchanted
@5 roses – yes, or laced with cunning psychotropic additives.
@5 roses – Yes, but he still asked for it first. The White Witch didn’t just offer him Turkish Delight, she asked him what he wanted, and he asked for Turkish Delight. If he’d asked for chocolate, she would have given him enchanted chocolate.
I always thought this was white nougat because the same word can be used for both in German, but it seems to be something else.
Well, that certainly clears up a lot of misconceptions. So lokum aka “Turkish Delight” is like halwa and other such recipes of the wider Middle East, easy in theory but very, very difficult to get right?!?
Myself, I’d always wondered why he just didn’t ask for Amsterdam cannabis cookies and full speed ahead and damn the torpedoes, sir!!!
I always assumed Edmund’s willingness was for three reasons: #1 Rationing of WW2 #2 He’s a brat kid who doesn’t understand the repercussions and #3
I figured enchanted Turkish Delight was a parallel drawn from myth and fairytale, wherein you do not eat the enchanted food of the enchanted realm lest bad things happen to you.
3,4: No, Turkish Delight, even from, or consumed in, Turkey, is pretty grim stuff in my experience. The kind you buy in Britain is pretty identical to the Turkish kind (what with Britain having a large Turkish population). Stinks of rose oil, dries your mouth out, unpleasantly chewy and fairly tasteless.
Now, baklava, that’s a different story. The Turks got it right with baklava.
Silly question. Because, Turkish Delight!
Baklava, ugh. Sickly sweet.
I had tried Turkish delight when I was young because of the Narnia books and it was terrible, seeing how it was one of the mass produced brands. But recently I found this place called Liberty Orchards which makes amazing Turkish delight with all different sorts of nut and fruit flavors (and rose-pistachio, which is light and delicate and delicious). If the witch had that for Edmund, I could understand the addiction even without magic.
There’s a place in Pike Place Market that sells freshly made Turkish Delight in a variety of flavors, including mango, strawberry, raspberry, rose, and a few others. The stuff is FABULOUS, and makes a person understand why the good Turkish Delight was what Edmund asked for, outside of the historical implications.
The Cadbury stuff that’s covered in chocolate? FLEE. It’s terrifying.
Heh, when I was little, we had an animated version of the Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe which I watched incessantly, and the Turkish Delight was animated as little cubes. I always assumed it was something soft and chewy. I’ve always wondered what it was actually like and what the big deal was. I had heard it wasn’t really that great but it could be that the people were talking about an imitation. It sounds like the kind of thing I’d like :) But the sugar rationing especially makes sense in context.
Turkish delight was the least confusing thing to me. How about perpetual Winter. They’re worried about is no Christmas, when they should be worrying about feeding themselves. You can’t grow any of the food they were eating in Winter, but Christmas and your ability to get presents, that’s what was really missing. <facepalm>
It took a while, but Randall Munroe finally got around to calling attention to this issue.
C.S Lewis was a Christian writer. Turkish Delight is a metaphor for how sin never truly satisfies. This link may also help. I’m not preaching, ok??? I’m just trying to provide an explanation to what Lewis was trying to explain: https://josephfranks.wordpress.com/2015/09/17/sin-never-satisfies-but-jesus-does/
So, like most of Narnia, it is symbolic too, and Edmund is confusing the thing with the substance, huh?
I’d forgotten that Edmund asks for Turkish Delight. I do know it has some associations with snow and the nativity for me, as we often got dates and Turkish Delight at Xmas, maybe because of their associations with the middle east?
In terms of the subtext. Most people will know that Lewis spent many years in a dysfunctional – and at one stage at least, physical – relationship with a much older woman, a woman to whom he was largely subvervient. Crucially Mrs Moore was a virulent atheist (Lewis met her before his conversion) so I guess I don’t need to labour the symbolic significance. That said, the notion that his faith helped him banish the baleful influence of Mrs Moore was just so much wishful thinking on his part – he wrote the LWW shortly after sticking her in a home, where she died of old age and dementia not long after.
Have you ever had Turkish delight from Turkey it’s no pun intended is enchanting it’s sweet with flavours so fresh it has a flaky covering if you’re ever in Turkey try it then you will know why he was in a state were he was willing to answer everything
I think most miss the point. Turkish delight had a spell cast upon it. It was the representation of what we are programmed to believe – (acceptance of an assumption – the enemy of certainty from observation of what works for the majority of all concerned – truth) and that we would sell our souls and have done so just to attain what another gets us to think we want. For example: we are programmed to want. To want a better job, to want a job, to have more money, to want love, to want this or that to be happy. And so some of us actually succeed in getting those things but then that goal is met – they want another goal, and another goal…another thing and another. but in doing so we are doing and giving someone – usually, the top elite what they want – control over what you do, think and ARE. Wanting just gets you more wanting. Worry is praying for more worry. Every emotion is giving back to you and taints the emotions of others – both positive and negative. The enlightened know this and focus not on wants but on BEING. TO BE OR NOT TO BE…reqally is the question. To be happy now, loving now, satisfied now especially in the midst of hell. And when a person does – they own hell, they own heaven and the gods must bow to the knee. to the majority, this seems sacrilegious, crazy. But you are what you use yourself as – its always a choice. The witch was the personification of evil. Evil’s greatest tool is belief. You believe – you create that life accordingly and will give anything for that life. But are you happy, healthy and prosperous all the time? No – that can’t be done? Is THAT what you believe?
Interesting.
What are you giving away for the short-lived pleasures that never seem to satisfy?
@23 How about WANTING to tell evil to go to hell, just for the sake of it?”
P.S: I know I am being pedantic here, but it’s the kind of thing I often go through with my own thought processes. I tend to self analyze a lot to the point where it can be called over analyzing
Got my answer, it was Turkish delight because that is what Edmund asked for. It could have been power or riches, still he betrayed his family.
Does anyone think it is creepy how cuddly the grown up witch is with this young boy?